We’ve long been critical of the economics of the proposed CentrePointe development just a few blocks away in downtown Lexington.
One of the least understood portions of the project is the element known as Tax Increment Financing, or TIF.
In essence, TIF allows cities and states to allocate future incremental tax revenues to finance today’s public improvements related to new economic development initiatives.
The recent changes to the CentrePointe project invite a reassessment of the CentrePointe TIF program.
::
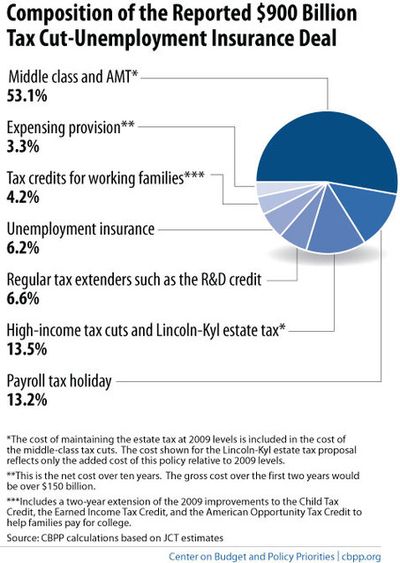
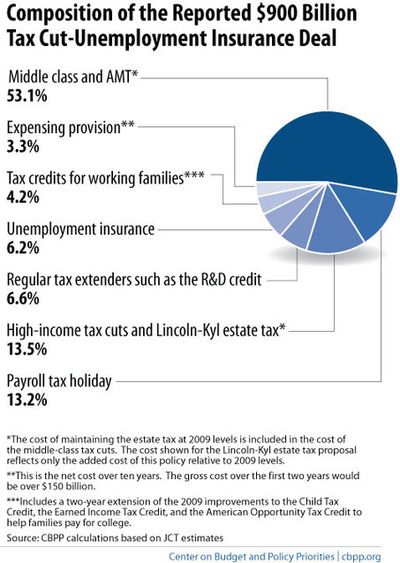
 CentrePointe’s TIF program would use future new tax revenues from the CentrePointe development to fund about $50 million in projects around CentrePointe.
CentrePointe’s TIF program would use future new tax revenues from the CentrePointe development to fund about $50 million in projects around CentrePointe.
These public initiatives would include:
- A new underground parking garage beneath Phoenix Park;
- Renovating Phoenix Park;
- Renovating the old Fayette County Courthouse (now the Lexington History Museum); and,
- Providing new infrastructure including storm sewers, sidewalks, and – according to the most recent renderings – a pedway which seems to cross Upper Street to (?!) McCarthy’s Irish Pub.
The state and city would issue some $50 million in 30-year bonds (i.e., public debt) to fund the initiatives. Over the course of the next 30 years, our governments would pay out some $100 million in principal and interest to the investors in the CentrePointe TIF bonds. The state would cover three-quarters of the total payments (about $72 million), and Lexington would cover the rest.
Then, the state and city would hope to use new taxes generated from CentrePointe over the next 30 years to offset the $100 million spent paying bondholders.
But is this a good investment of taxpayer dollars?
To get an informed answer, we need to dive deep into the business fundamentals of the CentrePointe TIF project.
(Note: What follows is financially ‘geeky’, but it is also critical to understanding how our money is invested.)
::
We have two major concerns with the CentrePointe TIF:
- The valuation methodologies used by the state and city are fundamentally flawed, and are not the standard for evaluating a long-term investment.
- CentrePointe will not generate the promised revenues, due to incredibly optimistic business model assumptions.
Let’s look at each of these concerns in succession.
Valuation Methodology
As far as we can tell, there have only been two evaluations of the public impacts of the CentrePointe project:
- A late 2008 assessment of CentrePointe done for Lexington by Morgan Keegan & Company which expected $211 million in total tax revenues over 30 years; and,
- An Economic Research Associates (ERA) report [PDF Link] done last summer for the state’s Cabinet for Economic Development, which expected nearly $70 million in tax revenues from CentrePointe for the state alone.
Of the two, ERA’s assessment is the more recent, more complete, and – in our judgment – more reliable. It is also the one which the state used to approve the CentrePointe TIF.
But, as mentioned above, there are deep flaws in how both of these reports valued the public benefits stemming from CentrePointe.
::
Businesses make investment decisions all the time: products, facilities, acquisitions, marketing, and so on.
When businesses evaluate an investment project, they look at how much they put in up front (‘the investment’) versus how much they can get out over time (‘the return’).
But when looking out into the future, most businesses lower the value of future earnings. In other words, the promise of $1 million next year isn’t worth as much as $1 million in-hand today. A lot of things can happen in the course of a year – inflation, disasters, competition, market shifts. And $1 million two years from now is worth even less, because there is even more risk of something happening.
Typically, stable and established businesses use an annual rate of around 10% to ‘discount’ future earnings. For example, if an investment generates a return of $1 million today, that is valued at $1 million. Simple enough. But if it promises another $1 million next year, that is worth just $900,000 to us today (i.e., 10% off of $1 million). The promise of $1 million two years from now is worth just $810,000 today, and earnings further in the future are given even steeper cuts in their valuations. So the promise of $1 million 30 years from now is worth just $42,000.
This ‘discounted cash flow’ method is the same standard that Warren Buffett and other investors use to evaluate how much to pay for an investment, and it is the financial equivalent of ‘a bird in hand is worth two in the bush’.
Depending on the kinds of risks an investment faces, the discount rate might be significantly higher.
When we purchased Lowell’s, we used a 20% discount rate. Even though Lowell’s was a solid business with loyal customers, we faced a number of uncertainties. Would we lose key employees? Would customers stay away in droves? Would things fall apart? Those things didn’t happen, but they posed very real risks as we purchased a new business.
With an especially speculative venture like CentrePointe, we would usually apply an annual discount rate of 20%. Or more.
So what kind of discount did Morgan Keegan and ERA apply to CentrePointe’s promised future tax revenues?
Zero.
Instead of incorporating the risks inherent with a project like CentrePointe, these assessments valued CentrePointe as if there were no risks at all. In these scenarios, the faint promise of $1 million in 2040 from CentrePointe was just as secure as having $1 million in our wallet today.
This is especially problematic, because so much of CentrePointe’s tax revenues were promised so far in the future, when a conventional valuation methodology would steeply cut their value.
For instance, in Morgan Keegan’s assessment, nearly half of CentrePointe’s tax benefits – over $100 million – came between 2030 and 2040.
::
The original report [PDF link] from Economic Research Associates (the state’s CentrePointe consultant) estimated that 30 years of tax revenues from CentrePointe would generate some $70 million for the state – while the state’s expenses for CentrePointe projects ran $72 million. So ERA projected that the state stood to lose $2 million on the CentrePointe TIF.
And that estimate derived from the faulty methodology we described above.
So what does the CentrePointe TIF look like when we apply standard valuation techniques? Let’s be generous, and apply the 10% annual discount rate reserved for stable investments to our analysis of CentrePointe. We’ll also use ERA’s estimated stream of future tax revenues.
Using a more conventional valuation of CentrePointe’s incremental taxes, they’re only worth about $25 million to the state, and an estimated $32 million overall.
In reality, the city and state would incur $50 million in public debt today for the CentrePointe TIF bonds, and only get back $32 million of that in future tax revenues. CentrePointe TIF is a poor investment which loses $18 million for taxpayers.
And that is even before we look at the stability of CentrePointe’s overly-optimistic business model…
Business Model Assumptions
A distinct pattern emerges in ERA’s assessment [PDF link] of the CentrePointe project for the state. At numerous points throughout the document, ERA hedges: they express skepticism about some element of the project, but then use the developer’s assertions about the project as ‘proof’ of its ultimate viability.
How ERA evaluates CentrePointe’s million-dollar condominiums is typical of these hedges (we’ve added emphasis in red):
“ERA approaches new luxury condominium projects in 2009 with a healthy degree of skepticism. […] Bank financing for new condominium construction has seized up. There is a very high degree of uncertainty in residential markets, especially high-end condominiums, across the U.S. And in recessionary times, introducing a luxury product where it has not been present before represents a considerable risk.
“However, there are two reasons for optimism in the CentrePointe Tower. First, the developers have pledged an all-equity transaction. This greatly reduces the risk that loans would have to be renegotiated in the middle of a deal, that payments would be missed, or that financing would be pulled at the last minute. While it does not eliminate all risks associated with financing, an all equity transaction greatly reduces the risks and complications of development in this difficult market.
“The second reason for optimism is that the developers have reservations for 64 units, out of 91. While a reservation is less a commitment than a purchase contract, this is still an impressive level of sales for this stage of the process. With two-thirds of units reserved before construction begins, the developers have demonstrated there is demand for these types of units.”
Both of the reasons for optimism that ERA cites come directly from the developer’s tenuous assertions.
The ‘all-equity transaction’ refers to the developer’s dead mystery financier, whom the developer had claimed was putting up cash (the ‘all-equity’ part of the transaction) to back the development. Last week, the developer admitted that he was forced to pursue more conventional financing. Using ERA’s logic, this would greatly increase the risks to the project’s success.
The ‘reservations for 64 units’ refers to the handshake deals that the developer claimed for the old CentrePointe design. As we have previously documented, 64 ‘reservations’ stretches the bounds of credibility in a market which only sold 10 million-dollar properties in all of 2008. And last week, the developer trimmed the number of condominiums in the new design from 91 to 63.
(Update: As Beverly Fortune notes, the numbers haven’t gotten better for million-dollar residential properties: Only 8 sold in Lexington in 2009, and only 5 have sold thus far in 2010.)
With both ‘reasons for optimism’ now rendered impotent, how would ERA evaluate CentrePointe’s condominiums today?
ERA’s skepticism extends to every other major part of the project:
Offices: “Estimated rents of $26 per square foot would be about $6 per square foot higher than the current highest quoted rate in the market – a number that may be difficult to achieve given current market conditions and may require some concessions.”
Retail and Restaurant: “ERA believes that $27 per square foot is an aggressive ask in this market, especially in downtown.”
Hotel: “With a first year ADR [room rate] of $175 and RevPAR [revenue per available room] of $103 at 53 and 45 percent higher than any comparable properties in the market at the end of 2008, these metrics may be optimistic. […] Projected hotel occupancy as well, is projected by the developer to be nearly 10 percentage points higher than the 2008 year-end average of 61.9 percent.”
In evaluating the entire project, ERA says
“Traditional bank financing would be extremely difficult, if not impossible, to secure for a project of this scale at a time like this. […] If the project’s equity financing remains intact and the investors are satisfied with the projected return, then ERA does not see a market barrier to feasibility of the project.”
How would ERA evaluate CentrePointe’s feasibility now that the ‘equity financing’ has fallen through?
Not well, we suspect.
::
We took the liberty of re-running ERA’s estimates with more realistic (but still quite generous) assumptions:
- The developer estimated that he would spend about $250 million on the old CentrePointe design. While there are few specifics, he has used a figure of $200 million for the new design. We adjusted construction spending down by 20%.
- The developer assumed they could get higher occupancy levels (over 71%) even though they were charging 50% more per night than the Lexington hotel market.We adjusted hotel occupancy to market levels – a more reasonable 62%.
- The developer has claimed to be able to sell two-thirds of their condominiums at the outset of the project. We adjusted expectations down to about 20% at the outset, and we never expect full occupancy of the 63 condos without drastic reductions in property price.
- The developer assumes a $26 to $27 per square foot rate for its office, retail, and restaurant leases. We’ve adjusted those assumptions down by about 20%. Such an adjustment still leaves these CentrePointe spaces as the highest rents in the Lexington market.
These adjustments to the CentrePointe business model have a number of economic ripple effects: Lower spending, lower sales, lower profits, fewer jobs created, lower quality of tenants, and lower tax revenues.
Using these more realistic assumptions, our estimate is that CentrePointe will generate incremental state and local taxes worth only $21.5 million ($16 million of that would go to the state, and the remaining $5.5 million would go to Lexington).
::
As long-time critics of the CentrePointe project, we hear a common counter-argument: that CentrePointe is a private development on private property and that we and our community leaders have no business questioning the project.
CentrePointe is a private development on private property.
But CentrePointe also has a number of externalities that make it of public interest. It would require significant public investment in new infrastructure and facilities to support the new development.
And while TIF projects are targeted to public improvements, the reality is that about half of the $50 million publicly-financed CentrePointe TIF projects would most directly benefit CentrePointe’s developer: the parking garage, sidewalks, pedways, and other infrastructure.
It is highly unlikely that the developer would go forward with the project without the public subsidy of these elements – despite his prior threats to do so.
A second TIF reality is that the public bears a disproportionate part of the risk of the new development: In return for putting up $50 million of our money today, taxpayers are promised an unreliable trickle of future tax payments over the next thirty years.
So despite what many of CentrePointe’s defenders – including Lexington’s mayor – say, CentrePointe’s TIF program does amount to a public subsidy of the private development of CentrePointe.
And when we apply a realistic analysis, that CentrePointe TIF subsidy is a truly awful investment.
In return for committing $50 million in new debt (and paying another $50 million in interest on top of that), taxpayers get a return of just $21.5 million.
Local government would lose almost $7 million on its $12 million investment, while the state would lose $21 million on its $37 million investment.
And despite the developer’s indignant none-of-your-damn-business attitude toward public inquiry on CentrePointe, it clearly is a public issue with public dollars at stake. The CentrePointe TIF is little more than outright welfare for the developer and his project.
The CentrePointe TIF is a spectacularly bad public investment, and every attempt should be made to rescind the TIF approval.
The proposed redesign of CentrePointe should be a time for community leaders to rethink the community’s investment in CentrePointe.
At a time when our public budgets are under extreme duress, now is not the time to spend extravagantly on a wildly speculative private development such as CentrePointe.
No responsible business would make this kind of investment. Our governments shouldn’t either.
 And like most great designs, it poses elegant solutions to several problems at once. Here are a few highlights which caught our attention:
And like most great designs, it poses elegant solutions to several problems at once. Here are a few highlights which caught our attention: